1. Raw Material Preparation
- Pulp Selection: The main raw materials for white cardboard production are wood pulp and waste Paper pulp. A combination of virgin and recycled fibers ensures a balance between quality and cost-effectiveness.
- Pulping: The raw materials are processed into pulp through mechanical, chemical, or semi-chemical methods. This process breaks down the fibers into a slurry, which will form the basis for the paper production.
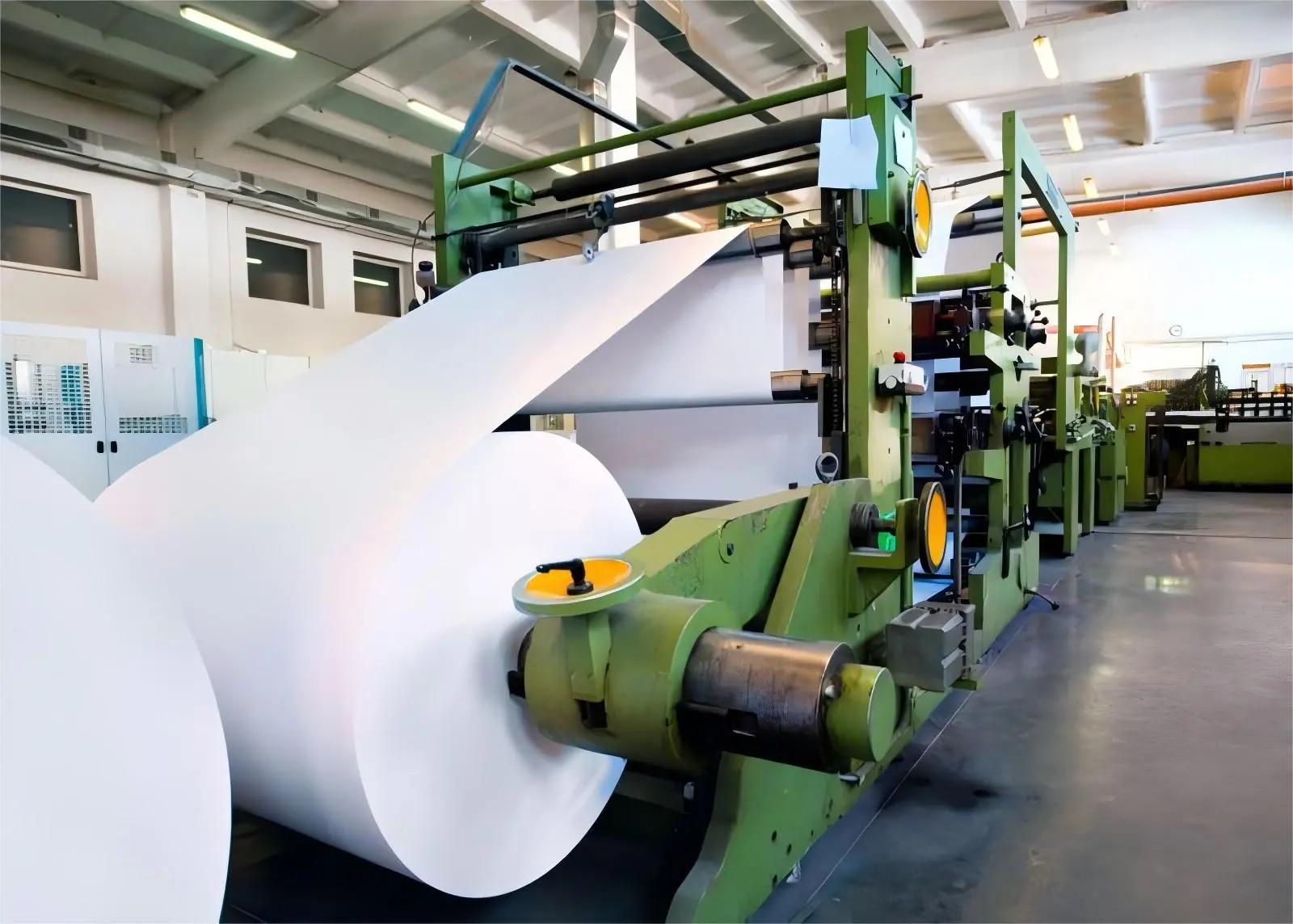

2. Pulp Refining
- Refining: The pulp undergoes refining to enhance its fiber characteristics. The refining process increases the bonding ability of fibers, which directly impacts the strength and smoothness of the final product.
- Blending and Adjustments: Different grades of pulp are blended and adjusted to meet the desired quality of the white cardboard. Various additives, such as fillers, dyes, and sizing agents, are mixed to improve brightness, opacity, and surface properties.
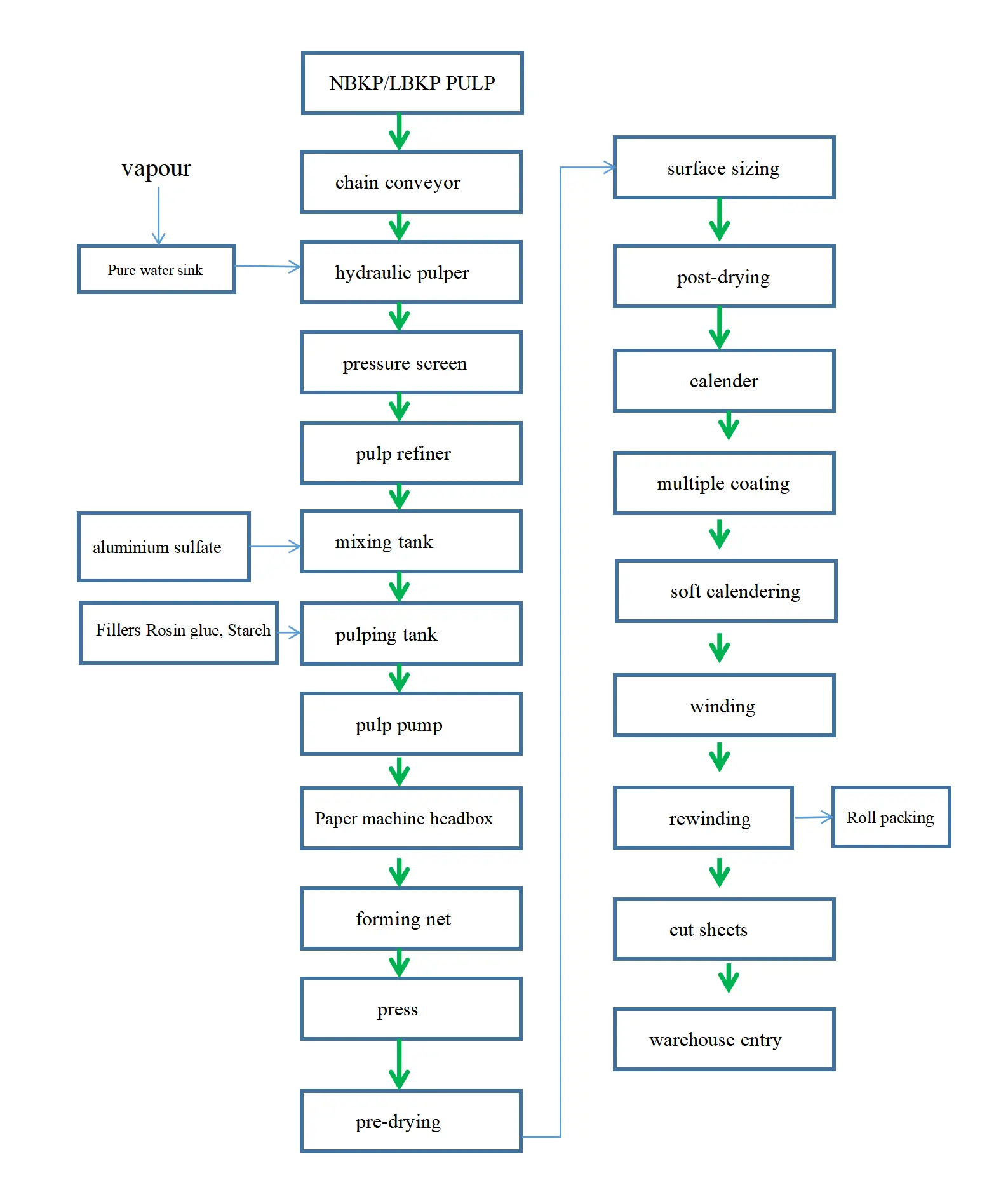
3. Papermaking Process
- Sheet Formation: The refined pulp mixture is transferred to a Fourdrinier or cylinder machine, where it is evenly distributed across a wire mesh to form a wet sheet. The water drains through the mesh, and a fibrous mat begins to take shape.
- Pressing: The wet sheet passes through a series of press rollers to remove additional water. This step increases the density of the sheet, ensuring a compact and even thickness.
- Drying: The pressed sheet moves through heated cylinders or drying sections, further removing moisture until the paper reaches the desired dryness level.
4. Surface Treatment
- Coating: For white cardboard, a coating layer is applied to improve surface smoothness, printability, and brightness. The coating mixture typically consists of kaolin, calcium carbonate, and other pigments.
- Calendering: The Coated sheet passes through a calendering process, where it is pressed between smooth rollers to achieve a uniform thickness and enhance the surface glossiness.
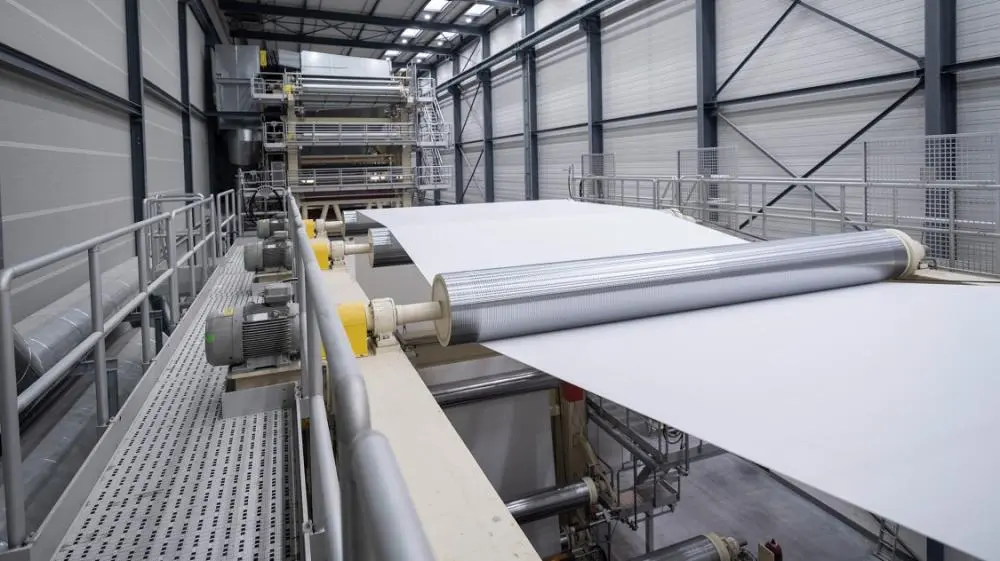

5. Reeling and Cutting
- After the calendering process, the paper is reeled onto large rolls. These rolls are then cut into sheets or smaller rolls according to customer requirements. Precision cutting ensures consistent dimensions and reduces waste.
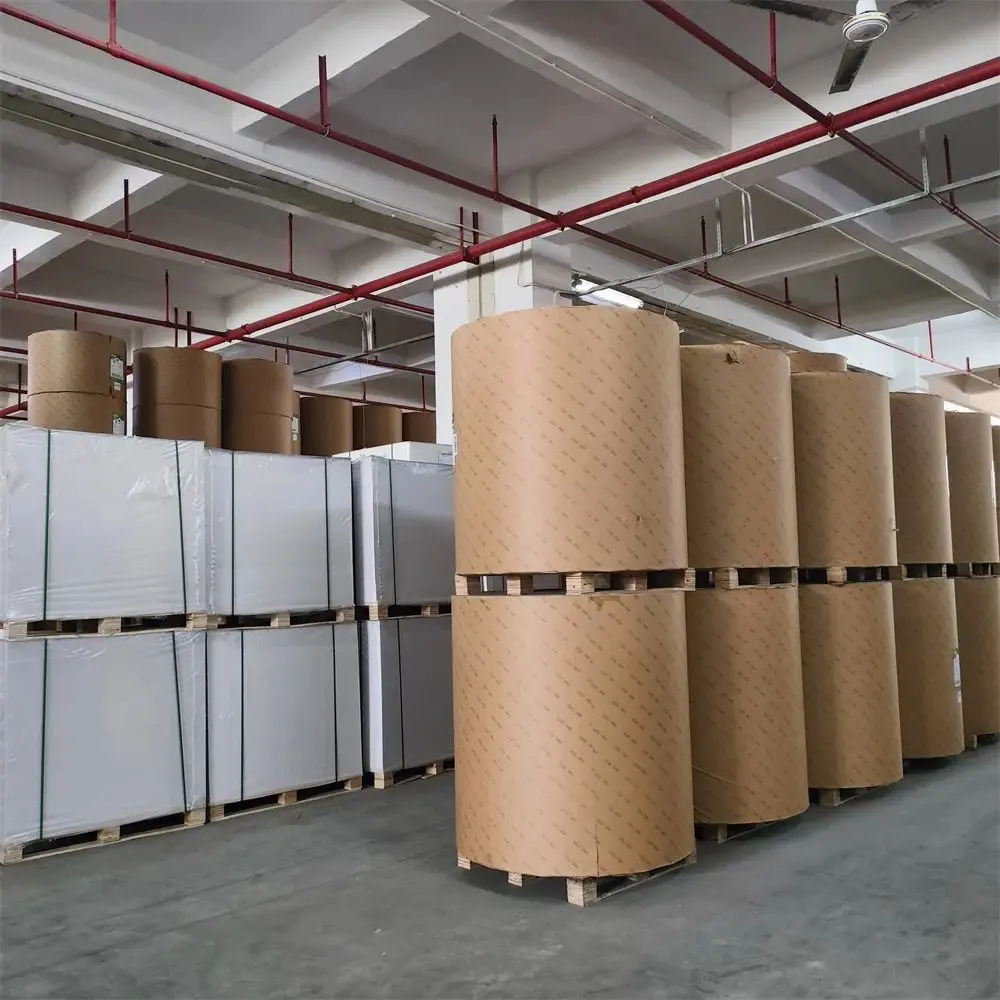

6. Quality Inspection and Packaging
- Inspection: The final product undergoes a thorough quality inspection to ensure it meets industry standards. Tests are conducted for thickness, brightness, opacity, and smoothness.
- Packaging: Once the paper passes quality checks, it is packed in moisture-resistant packaging and prepared for shipment to ensure the paper remains in optimal condition during transportation.
The production of white cardboard involves a complex series of steps, from raw material preparation to surface treatment and packaging. Each step is designed to achieve the high-quality standards required for applications such as packaging, printing, and high-end graphic use. The careful control of each stage ensures that the final product possesses the desired properties of stiffness, smoothness, and printability.




