1.Basic Concept Analysis
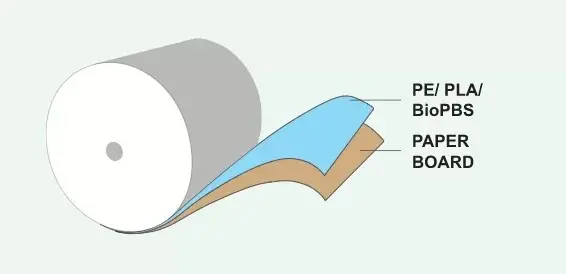
Laminated Paper refers to a composite material formed by coating a layer of plastic film (such as PE, PLA, PP, etc.) on the surface of the original paper (such as white card paper, cultural paper, or kraft paper) through the extrusion coating process. This layer of film gives the paper waterproof, oil-resistant, and highly sealable functions, and is widely used in the food packaging field. While MG food-grade kraft paper is the full name of “Machine Glazed Food Grade Kraft Paper”, which is a high-strength, unbleached or lightly bleached paper with good breathability and mechanical strength, meeting the safety standards for food contact materials.
2.Comparison of Structure and Manufacturing Process
|
Item |
Laminated Paper |
MG Food-grade Kraft Paper |
|
Structural Composition |
Original Paper + Plastic Film Layer (such as PE/PLA) |
Single-layer Paper (wood pulp or recycled pulp) |
|
Manufacturing Process |
Original Paper Splicing → Heating and Drying → Plastic Melt Extrusion → Extrusion Coating → Cooling and Stabilization → Splicing → Rolling Up |
Paper Pulping → Paper Making → Glazing → Drying → Finished Product |
|
Composite Material? |
Yes |
No |
Explanation: Laminated paper is a composite material that relies on the plastic film to enhance functionality; while MG food-grade kraft paper achieves physical properties through the natural fiber structure, maintaining the essence of pure paper.

3.Performance Comparison Analysis
|
Performance Indicators |
Laminated Paper |
MG Food-grade Kraft Paper |
|
Waterproofness |
Excellent (especially PE/PP laminated) |
Generally (high water absorption) |
|
Oil Resistance |
Excellent (suitable for oily foods) |
Generally |
|
Temperature Resistance |
Dependent on the film material (PE about 60℃, PLA about 50℃) |
Good, suitable for normal temperature use |
|
Printing Adaptableness |
Good (especially after corona treatment) |
Good, but attention should be paid to ink absorption control |
|
Environmental Friendliness |
Generally (depending on the film material, PLA is biodegradable) |
Excellent (fully recyclable, compostable) |
|
Air Permeability |
Poor (film layer blocks gas) |
Good (suitable for ventilation packaging) |
|
Mechanical Strength |
High (paper-plastic combination) |
Highly (natural kraft paper characteristics) |
|
Cost |
Moderately High (including film material cost) |
Lower |
4.Food Safety Comparison
|
Item |
Laminated Paper |
MG Food-grade Kraft Paper |
|
Is Food Grade? |
Yes (must be clearly labeled as food grade) |
Yes (natural food-grade material) |
|
Can It Be Directly Contacted with Food? |
Yes (must comply with GB 4806 standards) |
Yes |
|
Additive Risk |
Yes (plastic film may contain additives) |
No |
|
Particle Shedding Risk |
Yes (film layer peeling risk) |
No |
Explanation: Although high-quality laminated paper can also meet food contact safety standards, under extreme conditions (such as high temperature, long-term storage), there may be risks of film layer peeling or additive migration. In contrast, MG food-grade kraft paper has simpler components and is more stable, making it more suitable for enterprises that prioritize food safety.

5.Environmental Depth Comparison
|
Laminated Paper |
MG Food-grade Kraft Paper |
|
|
Recyclability |
Dependent on the film material (PE difficult to recycle, PLA requires professional treatment) |
Fully Recyclable |
|
Biodegradability |
Dependent on the film material (PLA can be industrial composting) |
Fully Natural Decomposable |
|
Carbon emissions during production |
Relatively high (involving plastic production) |
Lower (pure plant fibers) |
|
Difficulty in post-processing |
Complex (requires sorting) |
Simple (direct disposal or recycling) |
6. Suggestions for selection: How to make reasonable decisions based on requirements?
|
Usage requirements |
Recommended materials |
|
Seeking environmentally friendly, recyclable, and cost-effective |
MG food kraft paper |
|
Need for waterproof, oil-proof, and sealing functions |
Laminated paper (especially PLA laminated paper) |
|
For food contact packaging |
PE laminated paper (compliance is sufficient) / PLA laminated paper (more environmentally friendly) |
|
For medical/electronic industry protection |
Laminated paper (requires special membrane materials) |
|
For basic food packaging requirements |
MG food kraft paper |
|
For beautifully printed packaging |
Laminated paper (better printing effect) |
7. Conclusion
Laminated paper and MG food kraft paper each have their advantages and disadvantages, and they excel in different application scenarios. With stricter global environmental regulations and enhanced consumer environmental awareness, packaging materials that are degradable, recyclable, and reusable will become the mainstream direction. Although laminated paper still has advantages in functionality, its environmental treatment problems have become increasingly prominent. Therefore, PLA and other bio-based laminated papers are expected to become an important development direction to replace traditional PE laminated papers, while MG food kraft paper, due to its natural and environmentally friendly properties, will continue to expand its market share in food packaging, daily necessities, and cultural and creative products.