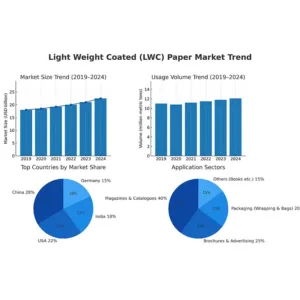
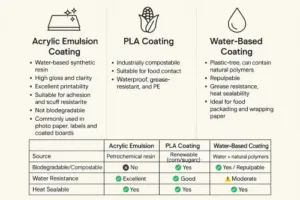
1. What is Glassine Paper?
Glassine paper is a super-calendered, smooth, and translucent paper known for its oil resistance, moisture barrier, and clean aesthetics. It is widely used in:
-
Release liners for self-adhesive labels, tapes, and medical applications.
-
Protection layers for books, artworks, and photographs.
-
Food packaging, especially for bakery products, confectionery, and meat separation.
-
Laboratory weighing papers due to its anti-static and non-stick properties.
-
Philately and specimen storage, like stamp envelopes and slide pouches.


2. Types of Glassine Paper
Glassine paper can be classified based on manufacturing process and functional features:
-
Super-calendered glassine: High transparency and smooth surface.
-
Silicone-Coated glassine: Enhanced release properties.
-
Bleached & unbleached: Bright White or natural beige.
-
Standard & antistatic grades: For general or precision applications.
-
Colored glassine: Customized for branding needs.
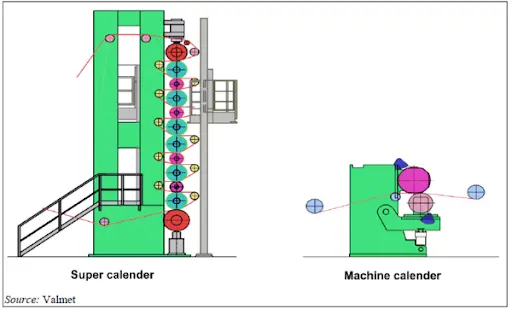
3. Common Basis Weights
|
Type |
Basis Weight (g/m²) |
Typical Applications |
|
Lightweight (Tissue) |
17–40 |
High-transparency interleaving, lightweight food separators |
|
Standard |
40–60 |
General food packaging, standard release liner |
|
Medium |
60–90 |
Label liners, tape liners |
|
Heavy |
90–200 |
Specialty labels, heavy-duty release applications |
4. Bag-Making Feasibility and Process Recommendations
4.1 Direct Bag Making
-
Challenges: Smooth, low-porosity surface affects adhesive bonding.
-
Solutions: Use high-tack adhesives, adjust temperature & pressure. Heat sealing requires additional sealant layers or lamination.

4.2 Wax-Coated Glassine
-
Pros: Improved oil and moisture resistance.
-
Cons: Reduced surface absorbency affects glue adhesion.
-
Tips: Use specialized adhesives or mechanical locking (e.g., folding designs).
4.3 Silicone-Coated Glassine
-
Pros: Excellent release properties.
-
Cons: Very difficult for adhesives to bond.
-
Workarounds: Partial de-siliconization, adhesive on non-silicone areas, or mechanical methods like stapling or stitching.

5. Recommended Processing Solutions
To achieve high-quality glassine bags:
-
Adhesive Sealing: Hot-melt adhesives with reinforcing designs.
-
Heat-Seal Inner Film: Laminate with PE/PLA films for secure heat sealing.
-
Mechanical Structures: Use interlocking folds, stitching, or perforations.
-
Small-Batch Testing: Optimize adhesive volume, pressure, and speed.
6. Conclusion
-
Uncoated and wax-coated glassine are viable for bag-making with proper adhesive and design adjustments.
-
Silicone-coated glassine requires advanced processing and is not recommended for conventional adhesive sealing.
-
Best practice: Laminate glassine with PE/PLA film to ensure reliable sealing and enhance functional properties.